
NAVYPEDIA
 Support the project with paypal
Support the project with paypal
Photo

Canberra 1928
Ships
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 1950- C01 | John Brown, Clydebank, UK | 26.8.1925 | 17.3.1927 | 24.4.1928 | sold for BU 1955 | |
| Canberra | John Brown, Clydebank, UK | 9.9.1925 | 31.5.1927 | 10.7.1928 | sunk 9.8.1942 |
Technical data
| Displacement standard, t | 9750 - 9870 (about 10900 finally) |
|---|---|
| Displacement full, t | 13400 - 13540 (14490 - 14910 finally) |
| Length, m | 179.8 pp 192.0 - 192.9 oa |
| Breadth, m | 20.8 |
| Draught, m | 6.25 deep load (6.71 - 6.88 finally) |
| No of shafts | 4 |
| Machinery | 4 sets meBrown-Curtis geared steam turbines, 8 Admiralty 3-drum boilers |
| Power, h. p. | 80000 |
| Max speed, kts | 31.5 |
| Fuel, t | oil 3200 - 3400 |
| Endurance, nm(kts) | 13300(12) |
| Armour, mm | box protection to magazines: 111 - 25, belt: 25, bulkheads: 25, barbettes: 25, turrets: 25, deck: 38 - 25 |
| Armament | 4 x 2 - 203/50 Mk VIII, 4 x 1 - 102/45 QF Mk V, 4 x 1 - 47/40 Hotchkiss Mk I, 4 x 1 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk II, 2 x 4 - 533 TT |
| Complement | 685 - 710 |
Standard scale images
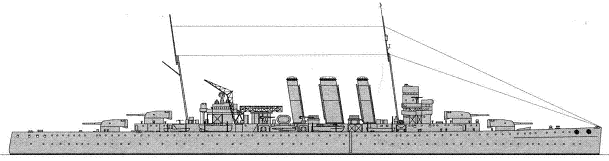
Canberra 1940
Graphics
Project history
First British cruisers designed according to limitations established for cruisers by Washington conference (10 000t standard displacement, no more han 203mm main guns). In comparison with the similar ships of other navies they were not so fast and protected however possessed the big endurance and good seaworthiness. They were intended, first of all, for protection of sea communications and hunting for raiders, instead of for operations with main forces. Five ships were built under 1925 programme. Two more ships were ordered by Australia.
Hull form in the cross-section plan resembled one accepted on last battlecruisers of Royal Navy (Courageous and Hood): above a waterline it was trapezoidal, transferred to blisters below. Ships had original box-shaped armour protection concentrated round the vital places. Main guns had maximal elevation angle 70°.
Protection
Underwater protection (bulges) was 1.6m in deep on British and 0.76m on Australian ships. Magazines were protected by 111 (102mm armour on 9mm plating)-25mm sides and 76-25mm platform deck. Machinery was protected by 25mm bulkheads and 32mm deck. Steering gear has 38-25mm horizontal protection.
Modernizations
1934, both: + 2 x 4 - 12.7/62
1935, Australia: + 1 catapult S-II-L, 1 Osprey seaplane
1935 - 1939, Australia: new 114mm belt 1.8m in height abreast machinery and transmitting station was fitted. 102mm internal plating was added to the sides of boiler room fan compartments. New catapult E-IV-H for Walrus seaplane was fitted; + 1 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII
1939, both: - 4 x 1 - 47/40
12/1940, Australia: - 4 x 1 - 102/45, 2 x 4 - 533 TT; + 4 x 2 - 102/45 QF Mk XVI, type 286 radar
early 1941, Canberra: + 4 x 1 - 102/45 QF Mk V, radar
6/1942, Canberra: - 4 x 1 - 40/39; + 2 x 8 - 4.39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 5 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
10/1942, Australia: - 1 x 4 - 40/39; + 2 x 8 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII
late 1943, Australia: - 4 x 1 - 40/39, 2 x 4 - 12.7/62, type 286 radar; + 7 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, type 273, type 281 radars
3/1944, Australia: - catapult and seaplanes, 7 x 1 - 20/70; + 7 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
2/1945, Australia: - 1 x 2 - 203/50; + 2 x 8 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 2 x 4 - 40/56 Bofors Mk 1.2, 2 x 2 - 40/56 Bofors Mk 1.2, 2 x 1 - 40/56 Bofors Mk 1.2, type 284, type 285 radars
late 1945, Australia: - 7 x 2 - 20/70
Naval service
Canberra was demolished by gunfire of Japanese cruisers Chokai, Aoba, Kako, Furutaka and Kinugasa in battle off Savo 9.8.1942 and sunk in 7 hours.
 HOME
HOME FIGHTING SHIPS OF THE WORLD
FIGHTING SHIPS OF THE WORLD AUSTRALIA
AUSTRALIA CRUISERS
CRUISERS AUSTRALIA heavy cruisers (1928)
AUSTRALIA heavy cruisers (1928)
