
NAVYPEDIA
 Support the project with paypal
Support the project with paypal
Photo
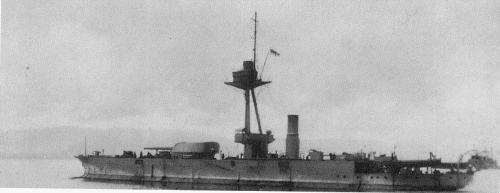
Abercrombie 1919
Ships
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admiral Farragut, 5.1915- M1, 6.1915- General Abercrombie, 6.1915- Abercrombie (ex-Farragut) | M01, M00 | 472 | Harland & Wolff, Belfast | 12.12.1914 | 15.4.1915 | 5.1915 | disarmed 6.1920, sold for BU 6.1927 |
| General Grant, 5.1915- M2, 6.1915- Havelock | M02, M05 | 473 | Harland & Wolff, Belfast | 12.12.1914 | 29.4.1915 | 5.1915 | disarmed 6.1920, sold for BU 6.1927 |
| M3, 6.1915- Lord Raglan, 6.1915- Raglan (ex-Robert E. Lee) | M09, M03, M14 | 476 | Harland & Wolff, Govan | 1.12.1914 | 29.4.1915 | 6/1915 | sunk 20.1.1918 |
| Stonewall Jackson, 5.1915- M4, 6.1915- Earl Roberts, 6.1915- Roberts | M08, M04, M1A | 991 | Swan Hunter, Wallsend | 17.12.1914 | 15.4.1915 | 5.1915 | test ship 5.1921, sold for BU 9.1936 |
Technical data
| Displacement normal, t | |
|---|---|
| Displacement full, t | 6150 |
| Length, m | 102.0 |
| Breadth, m | 27.4 |
| Draught, m | 3.10 |
| No of shafts | 2 |
| Machinery | Abercrombie, Havelock: 2 VQE, 2 Babcock & Wilcox boilers Raglan: 2 4-cyl. VTE, 2 Babcock & Wilcox boilers Roberts: 2 VTE, 2 Babcock & Wilcox boilers |
| Power, h. p. | Abercrombie, Havelock: 2000 Raglan: 2310 Roberts: 1800 |
| Max speed, kts | Raglan: 6.5 Roberts: 6 |
| Fuel, t | coal |
| Armour, mm | inner belt: 102, bulkheads: 102, barbette: 203, turret: 254 (face), deck: 51 - 25 |
| Armament | 1 x 2 - 356/45 BL Mk II, 2 x 1 - 76/50 12pdr 18cwt QF Mk I, 1 x 1 - 47/50 3pdr Vickers Mk I, 1 x 1 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk II, 4 x 1 - 7.7/87, intended to carry 1 seaplane (Short 166 on Roberts in 1915, Schneider on Abercrombie in 1916 and Short 184 on Raglan in 1917) |
| Complement | 198 |
Standard scale images
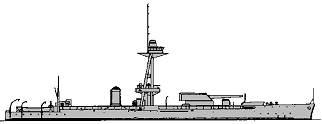
Roberts 1915
Graphics
Project history
The makeshift fleet of old battleships and gunboats which bombarded the Belgian coast in October 1914 showed clearly that whatever opportunities might be presented for warships to influence events ashore, the Royal Navy lacked ships suited to the task. Thus when on 3 November 1914 the President of Bethlehem Steel, Charles M. Schwab, called on Winston Churchill to offer four twin 356mm turrets, the First Lord of the Admiralty saw the possibility of using them for shore bombardment. The guns were destined for the Greek battleship Salamis but Schwab recognized that they would never get through the British blockade, and was quite happy to sell them to the British instead. Literally the following day the DNC was instructed to investigate the building of two 'armoured monitors' with a draught of 3.05m, within four months. The design, although pushed through very rapidly, incorporated the new anti-torpedo 'bulges' but in combination with the extremely bluff bow and stern, they made the monitors unwieldy and slow. Had Fisher been prepared to wait for the results of tank tests the proper power needed for 10ktss speed (roughly double what had been specified) would have been available in time, but construction was rushed ahead. The builders were mid to use whatever mercantile engines were available. To preserve secrecy the four monitors were referred to as Styx class, but in November 1914 American names were allocated to commemorate the US origin of their guns. But the Schwab deal, with its flagrant breach of neutrality, had already drawn strong State Department protests, and the ships were hurriedly renamed 31.5.1915 as M1-4. 19 (M1, 4) and 20 (M2, 3) June ships received new names, shortened 20-23.6.1915. Although called 'monitors' the new ships bore little resemblance to the low freeboard turret ships built in the 1860s, but the name had been applied to single-turreted ships built for coast defence and service in South American rivers, so the name was applied to the new ships. Their distinguishing features were a massive tripod mast and the large gun turret, and the diminutive funnel and bridge emphasized the bareness of the hull. All except Raglan had two derricks at the after end of the forecastle deck for handling seaplanes, making them the first British warships designed to carry aircraft. The secondary guns were carried below the forecastle, behind hinged bulwarks ahead of the 356mm turret. In addition they carried a single 3pdr and a 2pdr pom-pom for air defence.
Protection
There were bulges in role of underwater protection. Machinery and magazine were protected by 102mm inner belt, 102mm bulkheads and 51-25mm deck.
Modernizations
1915 - early 1916, all: funnel uprising; - 2 x 1 - 76/50; + 2 x 1 - 76/50 12pdr 18cwt QF Mk I (AA)
1916, Raglan; 1917, Abercrombie: + 1 x 1 - 152/45 BL Mk XII
1916, Roberts: + 1 x 1 - 152/40 QF Mk II (AA)
1916 - 1918, Abercrombie: - 1 x 1 - 152/45; + 1 x 1 - 76/45 20cwt QF Mk I
1916 - 1918, Havelock: - 1 x 1 - 47/50, 1 x 1 - 40/39; + 2 x 1 - 76/45 20cwt QF Mk I
1916 - 1918, Roberts: + 1 x 1 - 76/45 20cwt QF Mk I, 1 x 1 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk II
Naval service
Raglan was sunk 20.1.1918 by gunfire of German-Turkish cruisers Goeben and Breslau (127 casualties) off Imbros (Aegean). Roberts was sold in May 1921, but retained by Admiralty for trials. In 1925 she was considered for conversion to an airship mooring mast and fuelling point, and in the early 1930s was used for trials of underwater protection for new construction.
Many thanks to Wolfgang Stöhr for additional information on this page.
 HOME
HOME FIGHTING SHIPS OF THE WORLD
FIGHTING SHIPS OF THE WORLD UNITED KINGDOM
UNITED KINGDOM ABERCROMBIE monitors (4, 1915)
ABERCROMBIE monitors (4, 1915)
